UX is not a new phenomenon.
It has been around since the moment humans began to interact with tools and machines. It is found in everything that humans touch — ranging from tangible objects, such as a can opener, to the seamless experience of Amazon’s “1-Click” feature.
*Reference : https://uxdesign.cc/who-are-the-founding-fathers-of-ux-design-e41158dbc6e5
The History of UX Design
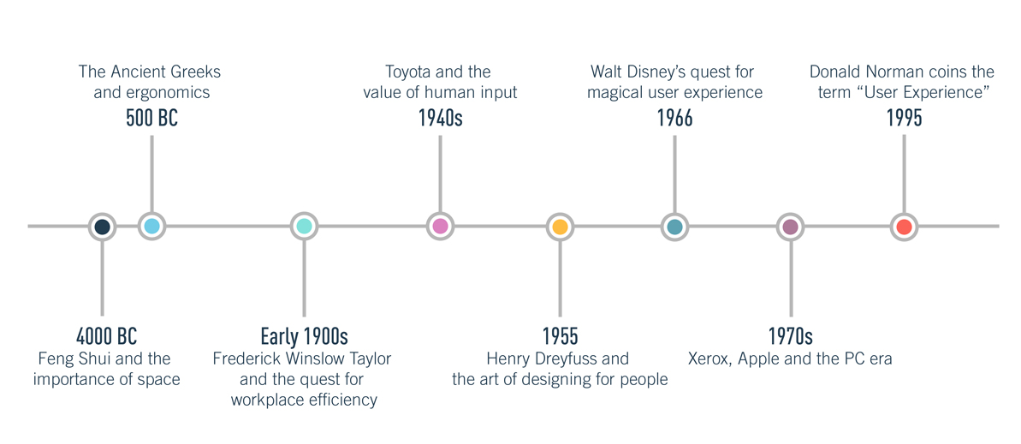
For centuries, humans have been seeking to optimize their surroundings for maximum user comfort. These days, the term UX design has strong digital connotations, often referring to apps, websites, software, gadgets and technology.
The 6 Principles Of Design, a la Donald Norman
There are many principles of design. But when it comes to web and interaction design, Donald Norman provides maybe the best six to abide by.
Donald Norman is one of the greats of computer human interaction and user-centred design (he did, after all, coin the term) and his principles are a good place to start with any design project.
*Reference : The Design of Everyday Things, Donald Norman
1) Visibility
Users need to know what all the options are, and know straight away how to access them. In the case of websites, this is an easy win.
2) Feedback
Every action needs a reaction. There needs to be some indication, like a sound, a moving dial, a spinning rainbow wheel, that the user’s action caused something.
3) Affordance
Affordance is the relationship between what something looks like and how it’s used.
4) Mapping
Mapping is the relationship between control and effect. The idea is that with good design, the controls to something will closely resemble what they affect.
5) Constraints
Constraints are the limits to an interaction or an interface.
6) Consistency
The same action has to cause the same reaction, every time.
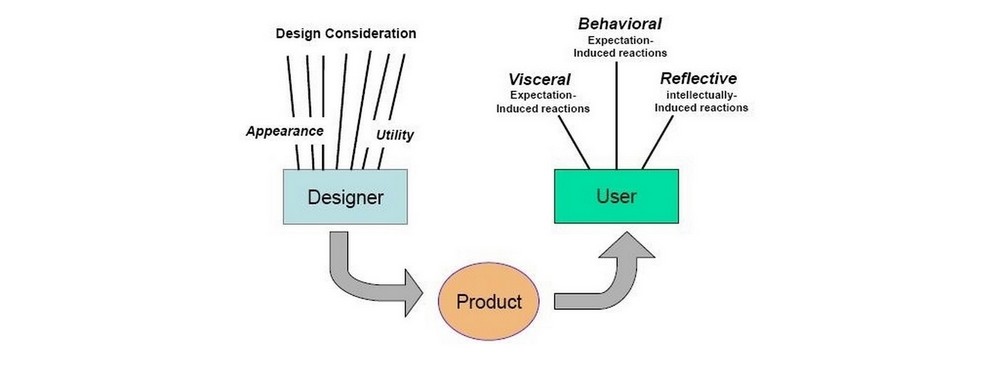
Norman’s Three Levels of Design
In Emotional Design: Why we love (or hate) everyday things, Don Norman (a prominent academic in the field of cognitive science, design, and usability engineering) distinguishes between three aspects, or levels, of the emotional system (i.e. the sum of the parts responsible for emotion in the human mind), which are as follows: the visceral, behavioral and reflective levels. Each of these levels or dimensions, while heavily connected and interwoven in the emotional system, influences design in its own specific way.
*Reference : https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/norman-s-three-levels-of-design